Product backlog template
Streamline task management and prioritization with this customizable product backlog template.
BEST FOR
Project management
KEY FEATURES
Task planning
Prioritization
Pipeline management

What is a product backlog template?
A product backlog template is a standardized, reusable format in which product development teams can list their tasks, such as features to be added, for future development. If your team follows the Agile project management methodology, a product backlog informs the roadmap for your work.
Prioritization framework
A product backlog template enables teams to prioritize tasks based on their business value and urgency. This structured prioritization approach ensures your team works on the most critical items first.
During spring planning, this framework helps teams select the right items to work on next. Start maximizing productivity and delivering value faster.
Enhanced consistency
A product backlog template provides teams with a consistent structure for organizing and tracking tasks across a project. As an essential part of Agile project management, the backlog template ensures everyone understands how to document and format tasks, making it easier to maintain clarity across the entire team.
With this free product backlog template, you have a standardized approach that helps maintain consistency and reduce confusion.
What does the product backlog template include?
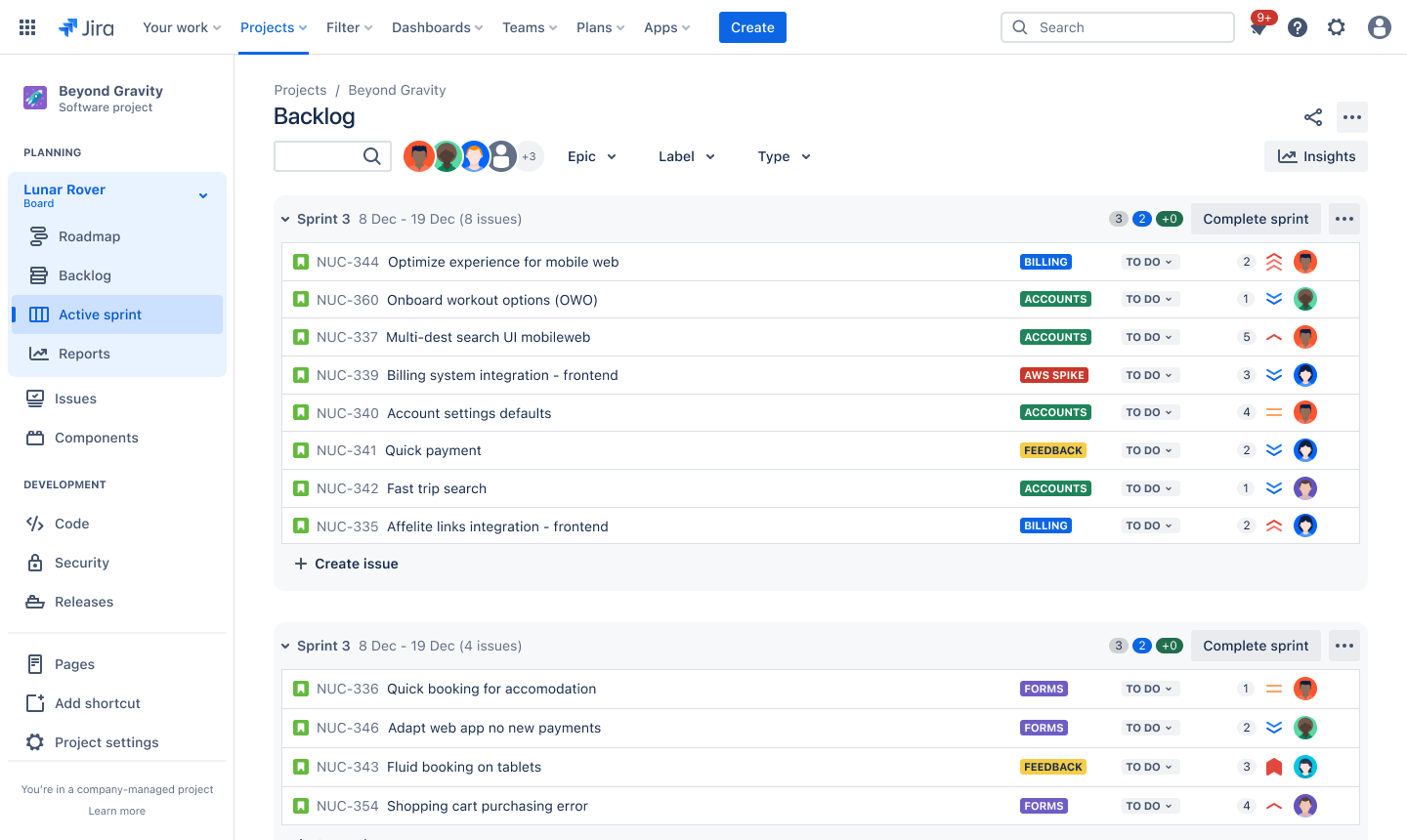
Sprint backlog
Use sprint backlogs to create your own product prioritization frameworks and easily see what your team will work on and when.
The sprint backlog highlights current tasks, aligns teams on short-term goals, and offers workflow flexibility to maintain project scope.
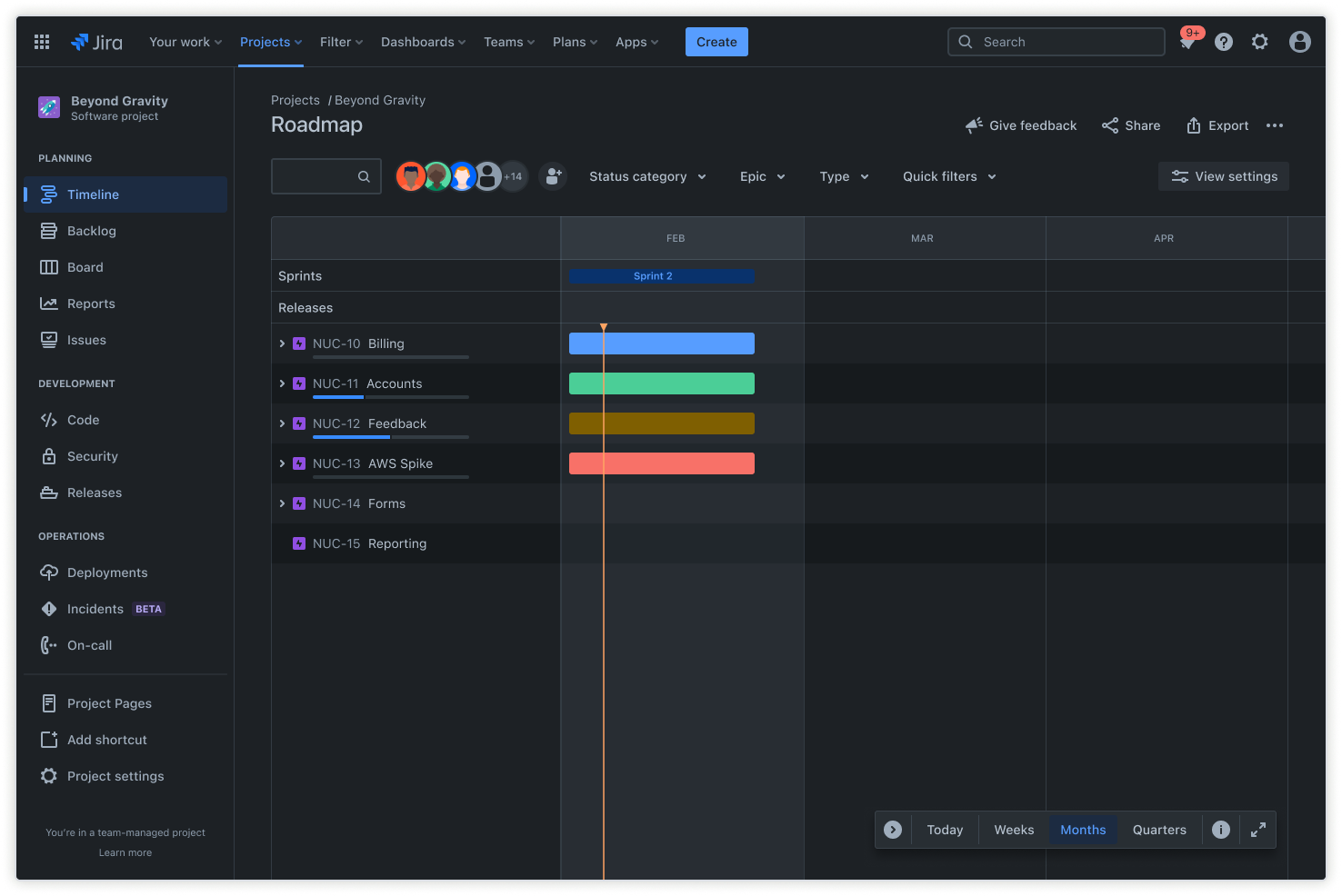
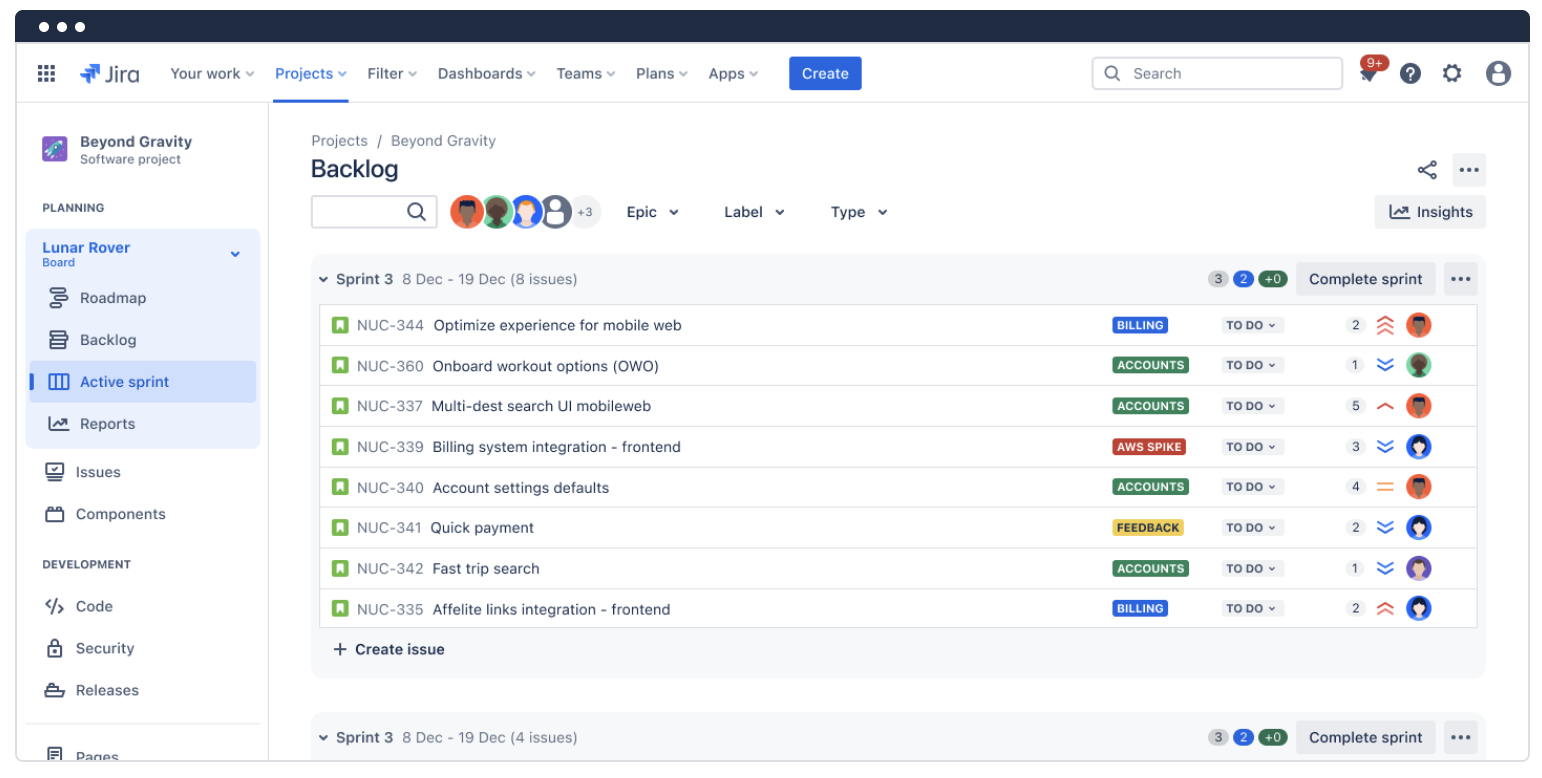
Product roadmaps
Build a customizable product roadmap (timeline) to plan work and track progress from a single view.
Add epics, map work items, set dependencies, and include releases to easily pivot and keep stakeholders in sync across the product development process.
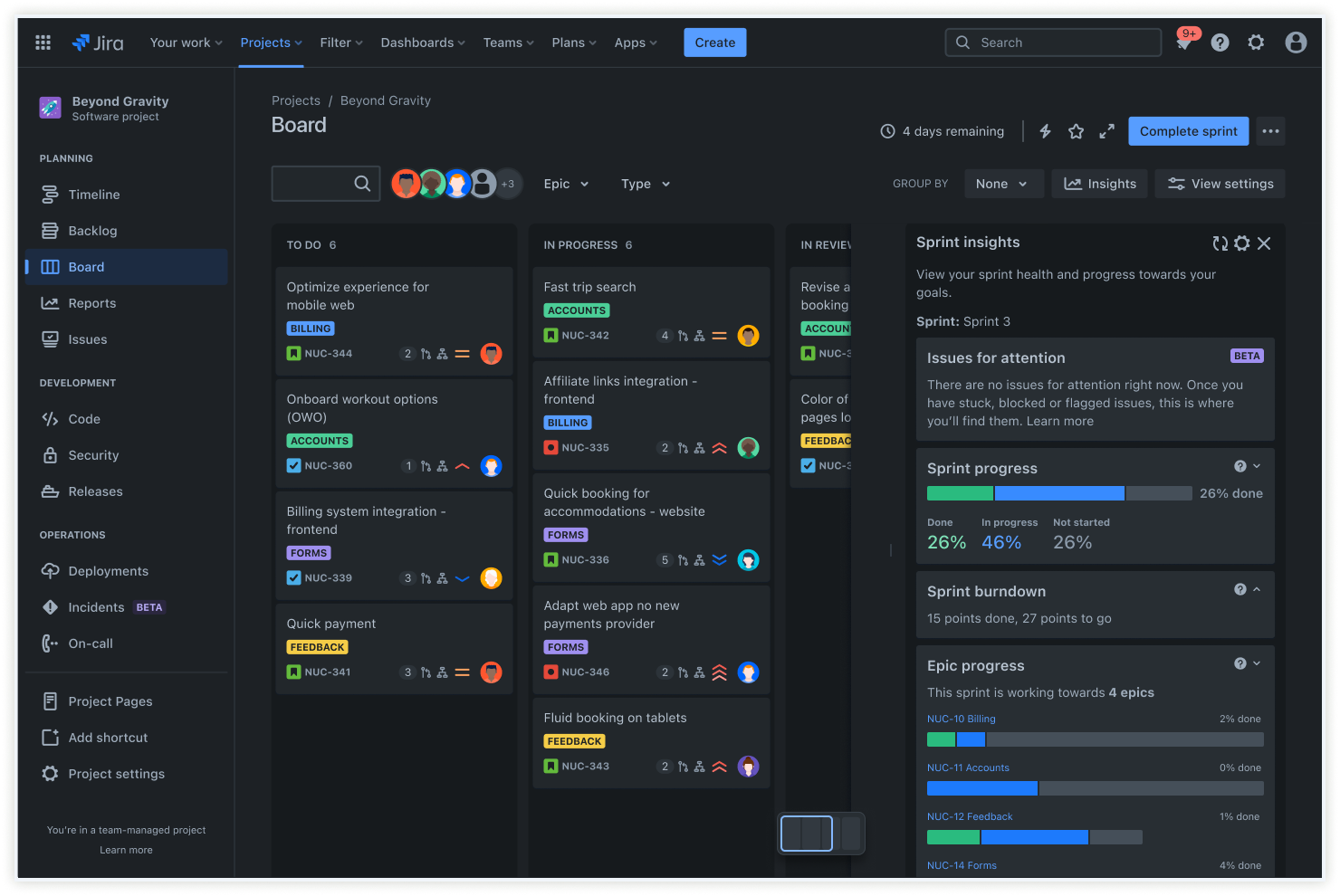
Insights
The sprint progress insights view provides real-time visibility into current sprint performance and momentum. Immediately assess the pace and identify potential bottlenecks without complex reports.
Optimize workloads and refine story points estimations for future planning and more accurate and achievable sprint goals.
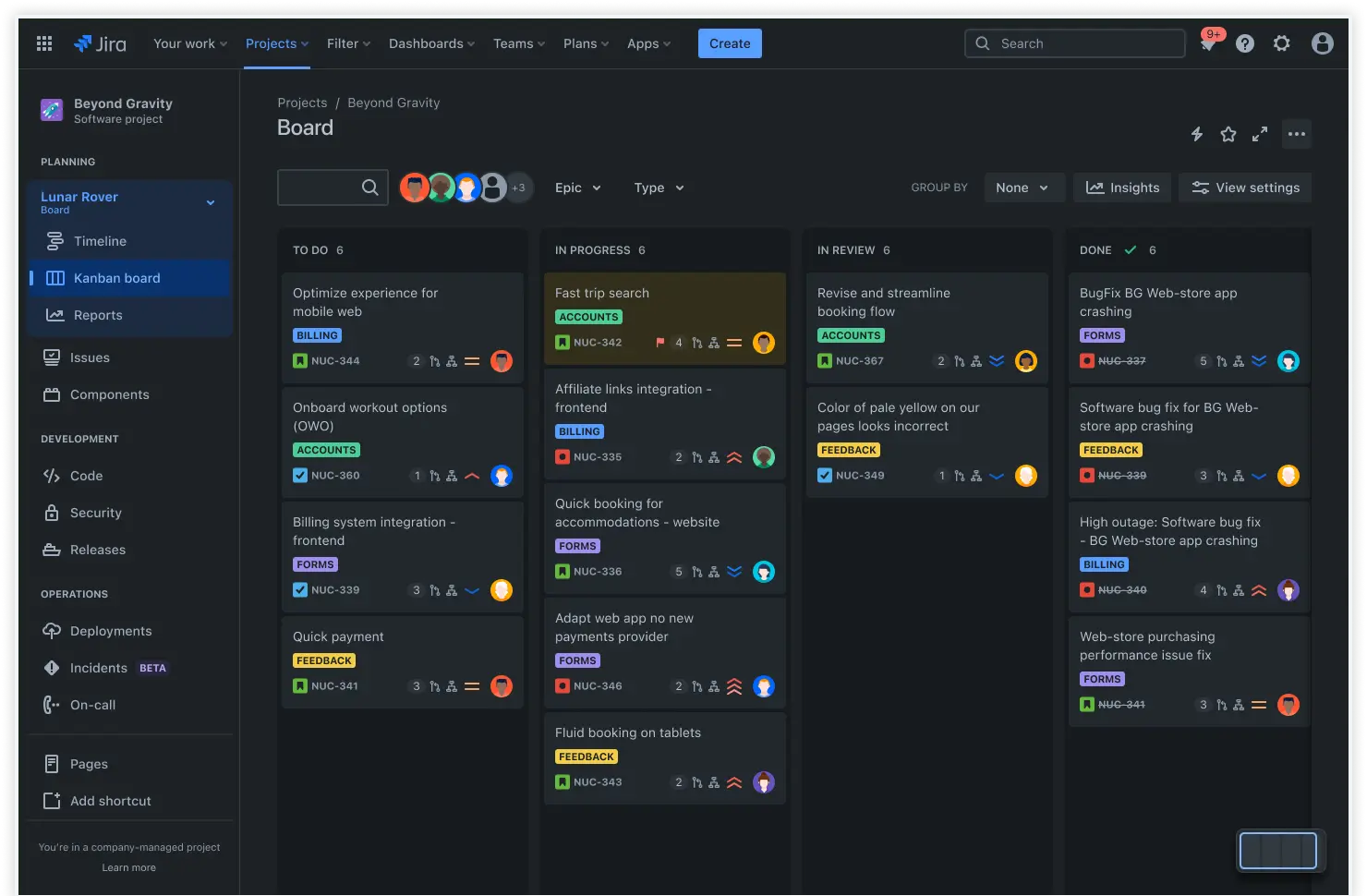
Kanban board
The Kanban board view helps teams visualize their workflow by organizing tasks into clearly defined stages.
Track progress, manage workloads, and help teams visualize work in progress to prioritize tasks or reduce bottlenecks.
How to get started with the product backlog template
- 1
Add your tasks
First, input your project's task names and/or descriptions. Naming consistency across the board will help your company in the long run. Some best practices include:
Use verbs to describe necessary actions.
Create specific names based on the feature or its capabilities, and be consistent.
Keep names short so tasks are easy to remember or find.
Don’t invent new words; use subject matter domain lingo common to your industry.
- 2
Add the start and due dates
Add the start and end dates for each task, as well as a delivery date for the entire project. However, deadlines aren't the only thing you need to worry about. You also need to:
Set clear deliverables for each task and due date.
Room for feedback loops from the necessary stakeholders.
Account for iterations in your timeline.
Limit the number of tasks within a single sprint.
Break down large tasks into smaller ones so the team can accomplish them more readily.
- 3
Designate roles
Next, assign tasks to your team. You want everyone to know who’s responsible for what. Clarity and autonomy empower your team and keep them engaged, so try to:
Assign tasks to team members with the necessary skills to accomplish them.
Encourage cross-collaboration among your team.
Provide clear instructions and feedback.
- 4
Note task priority
Your team can’t execute everything at once. They need to understand how dependent each task is on the others. The Lean methodology can help you here. Remember, you must order tasks based on importance so the team knows what to tackle first.
In Lean, you use a just-in-time approach, producing what you need when you need it.
Determine this using both customer and business needs.
- 5
Add the user story
Context is king. You need to provide a reason for the work you want your team to tackle. User stories not only give a purpose to the work, but they also remedy a pain point. Additionally, you'll want to provide context because:
User stories clarify how a feature or fix should work for the customer.
They're a statement from the user's perspective.
They clearly state who the users are, what they want the product to do, and its desired result.
- 6
Note the estimated effort
Effort estimation helps you set reasonable timelines and allocate resources appropriately. You can think of this as a forecast for how long the task will take. Remember to keep estimates at a high level, practice continuous improvement, and learn from past estimates. A few other things to consider include:
Note estimates in hours, days, or weeks.
You can use story points to estimate. The planning poker exercise helps. That’s when the team discusses a backlog item and comes to a consensus on a time estimate.
Based on previous and similar work, use this formula to calculate your pace: time estimated divided by the actual time taken.
- 7
Automate your work
Finally, automate manual labor that bogs your team in busy work. Various tools can accomplish this, such as:
GitHub: Automate your pull requests and updates through GitHub.
Jira Service Management: Connect dev or IT teams with customer service teams’ workflows.
Slack: Manage and automate ticketing and request workflows through Slack.
Related templates
Software Development
Kanban board template
Manage a continuous delivery of work on a powerful board.
Software Development
Scrum template
Visualize, track, and manage your work easily from sprint to sprint.